The GI Bill is one of the most generous education benefits programs in the country, providing crucial financial support for veterans pursuing college degrees or vocational training But how much does the GI Bill actually pay? The answer depends on which GI Bill program you use, your length of military service, the type of school you attend, and other factors
In this comprehensive guide, we’ll break down exactly how much you can expect to receive from the Post-9/11 GI Bill, the most widely used education program for veterans.
Post-9/11 GI Bill Overview
The Post-9/11 GI Bill, which started in 2009, gives veterans who served at least 90 days of active duty after September 10, 2001, a lot of benefits. Not like older GI Bills, the Post-9/11 version pays for more than just tuition and fees. Eligible veterans can receive money for housing, books, and other education-related costs.
The Post-9/11 GI Bill pays benefits directly to the student and their school. The main types of payments include:
- Tuition and fees payment sent directly to the school
- Monthly housing allowance sent to the student
- Annual book and supplies stipend sent to the student
- Rural benefit payment for those relocating from highly rural areas
- Yellow Ribbon payment to supplement costs at expensive private schools
How Much the GI Bill Pays for Tuition
After September 11, the GI Bill pays up to the full cost of tuition and fees at public colleges and universities in the same state. For 2023-2024, the maximum coverage is:
- Up to $27,120.05 per year at private and foreign schools
- Unlimited tuition and fees at public schools
- Up to $27,120.05 per year for vocational programs
Keep in mind that the Post-9/11 GI Bill pays a percentage of the maximum coverage based on your length of active duty service
- 100% for 36 months or more of active duty service
- 90% for 30-35 months
- 80% for 24-29 months
- 70% for 18-23 months
- 60% for 6-17 months
- 50% for 90 days to 5 months
So if you served for 2 years on active duty you would qualify for 80% of the full benefit.
Monthly Housing Allowance
One of the best things about the Post-9/11 GI Bill is that it pays for housing each month while you are in school. For 2023-2024, housing allowances are paid at the following rates:
- $2,109 per month for foreign schools
- Up to $1,054.50 per month for fully online programs
- Unlimited monthly allowance equal to the military BAH for your school’s location and your dependent status for in-person programs
Housing allowances are also prorated based on length of service and course load.
Book and Supply Stipends
The Post-9/11 GI Bill provides an annual book and supply stipend of up to $1,000 per academic year to help pay for books, laptops, supplies, and other equipment. This payment is sent directly to the student at the start of each term.
Total Potential Benefits
When you add up all the key payments – tuition, housing allowance, and book stipend – veterans can receive over $30,000 per year and up to $100,000 total under the Post-9/11 GI Bill.
For example, a veteran attending a 4-year public university full-time could receive:
- $27,000 per year in tuition payments
- $12,000 per year for a housing allowance
- $1,000 per year for books
That’s over $40,000 per year, and over $160,000 total over 4 years of school.
Of course, your individual benefits depend on the type of school, your service length, enrollment status, and other factors. But the Post-9/11 GI Bill can completely cover the cost of a public college degree for many veterans.
Yellow Ribbon Program
The Yellow Ribbon Program is an additional benefit that helps veterans attend private colleges or graduate programs that exceed the Post-9/11 tuition and fee coverage cap.
Here’s how it works:
- The school agrees to cover a portion of the tuition and fees that exceed the cap
- VA matches the school’s contribution
- Payments are made directly to the school
Over 5,000 colleges voluntarily participate in the Yellow Ribbon Program. This supplemental funding can make expensive private universities much more affordable for eligible veterans.
Transferring Benefits to Dependents
The Post-9/11 GI Bill also allows veterans to transfer benefits to their spouse or dependent children. This is a great option if you want to save your benefits for your kids to use.
To transfer GI Bill benefits, you must:
- Have at least 6 years of service in the armed forces
- Serve an additional 4 years from the date of transfer
- Designate dependents as beneficiaries
Benefits can be split between multiple dependents if you wish. The recipient dependents receive the same payments and benefits as the veteran would.
Applying for the GI Bill
To receive Post-9/11 GI Bill benefits, you need to submit an application to the VA. Here are the main steps:
- Gather documentation like your DD-214 discharge papers
- Submit application form 22-1990 to the VA
- Provide school certifying documents each term
- Verify enrollment status each month
Work closely with your school’s veterans office and the VA to ensure your benefits are processed correctly. You can submit documents and manage your benefits on the GI Bill website.
Choose the Right School
One of the great things about the GI Bill is that it opens up your education options. You can use your benefits at a wide range of VA-approved schools:
- Public and private colleges and universities
- Online colleges
- Vocational schools and non-degree programs
- Flight schools
- Apprenticeship programs
Do your research to choose an accredited program that provides the right mix of affordability, value, and support services. Many veterans choose public universities to maximize their GI Bill coverage. Online colleges offer flexibility for non-traditional students. And vocational programs like HVAC technician training can lead to solid careers.
Consider your career goals, budget, and learning preferences as you evaluate schools. Make sure to confirm the school and specific program are eligible for GI Bill benefits.
Work Study and Other Benefits
In addition to the major education payments, the GI Bill offers a few supplemental benefits:
-
VA Work Study – Earn an hourly wage for certain VA-related work like answering phones at the registrar’s office or VA hospital up to 25 hours a week.
-
Rural Relocation Allowance – Receive a one-time $500 payment if you must relocate from a highly rural area to attend school.
-
Tutorial Assistance – Get up to $100 per month, not exceeding $1,200 per year, for tutoring services if you are struggling with coursework.
GI Bill Deadlines
Most veterans need to use their Post-9/11 GI Bill benefits within 15 years of separation from active duty. Make sure to take advantage of this generous education package while you still qualify.
Spouses using transferred benefits must start school within 15 years of the service member leaving the military. Children’s eligibility ends on their 26th birthday in most cases, so encourage them to enroll directly after high school.
Choosing the Right GI Bill Program
While the Post-9/11 GI Bill is the most popular education program today, there are other GI Bill options:
-
Montgomery GI Bill – Active Duty (MGIB-AD, Chapter 30) – Older program that provides monthly benefit payments directly to the veteran.
-
Montgomery GI Bill – Selected Reserve (MGIB-SR, Chapter 1606) – Covers reservists with a 6-year service agreement.
-
Reserve Educational Assistance Program (REAP, Chapter 1607) – Provides benefits for reservists activated for at least 90 days after 9/11/2001.
-
Survivors’ and Dependents’ Assistance (DEA, Chapter 35) – Offers education benefits for qualified dependents of disabled or deceased veterans.
Make sure you apply for the right program based on your specific military background. In most cases, Post-9/11 provides the richest benefits.
Finding Other Aid Sources
Even generous GI Bill benefits may not cover all your education costs. Look into other financial aid options you can combine with your GI Bill:
-
Scholarships – Apply for private, institutional, community, and national scholarships for veterans and military families.
-
Pell Grants – Need-based aid for undergraduates.
-
Federal student loans – Low fixed-interest rates and income-based repayment.
-
Military tuition assistance – Some active duty service members receive TA benefits.
-
Employer tuition reimbursement – Many companies offer tuition benefits for employees.
Get the Most from Your GI Bill
The Post-9/11 GI Bill provides an amazing opportunity to earn a college degree or vocational credential with minimal debt. Make the most of this well-deserved benefit by:
- Researching approved schools and programs
Chapter 35 rates for survivors and dependents
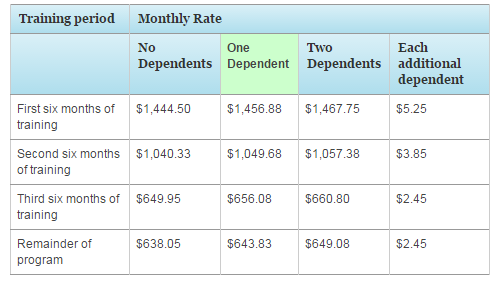
Find out how much money you can get through Survivors’ and Dependents’ Educational Assistance (DEA) to help you pay for education and training.
Find out how much money you can get through the Fry Scholarship to help you pay for tuition, housing, and other education costs.
Montgomery GI Bill Selected Reserve (Chapter 160 rates
Find out how much money you can get through the Montgomery GI Bill Selected Reserve (MGIB-SR) to help you pay for education and training.
GI Bill Housing Allowance Explained (BAH)
FAQ
How much money do you get from a GI Bill?
How much is the GI Bill monthly allowance?
|
State
|
MHA_NAME
|
MHA Rate
|
|
CA
|
SACRAMENTO
|
$2,844
|
|
CA
|
STOCKTON
|
$2,100
|
|
CA
|
VALLEJO/TRAVIS AFB
|
$3,342
|
|
CA
|
LOS ANGELES
|
$3,531
|
Does the GI Bill pay 100 percent?
Does the GI Bill cover 4 years of college?
How much does the GI Bill pay a month?
The Post-9/11 GI Bill also pays a monthly housing allowance based on the ZIP code of the location of the school or campus where you attend the majority of your classes. This stipend averages $1,934.80 a month but can exceed $2,700 depending on where you go to school.
How many months GI Bill benefits can I get?
Let’s break it down: 1.**Post-9/11 GI Bill (Chapter 33)**: – If you served on active duty after **September 10, 2001**, you may be eligible for the Post-9/11 GI Bill. – This program offers up to
How much does GI Bill increase a year?
Effective Aug. 1, those using the Post-9/11 GI Bill at a private or foreign school will see their maximum yearly GI Bill rate increase from $27,120.05 to $28,937.09. Those who are enrolled in flight schools will see their annual maximum GI Bill benefit increase from $15,497.15 to $16,535.46.
How much GI Bill do flight schools pay?
Those who are enrolled in flight schools will see their annual maximum GI Bill benefit increase from $15,497.15 to $16,535.46. You can be reimbursed up to $2,000 per test for licensing and certification tests. For national testing programs, there is no maximum amount of GI Bill reimbursement.