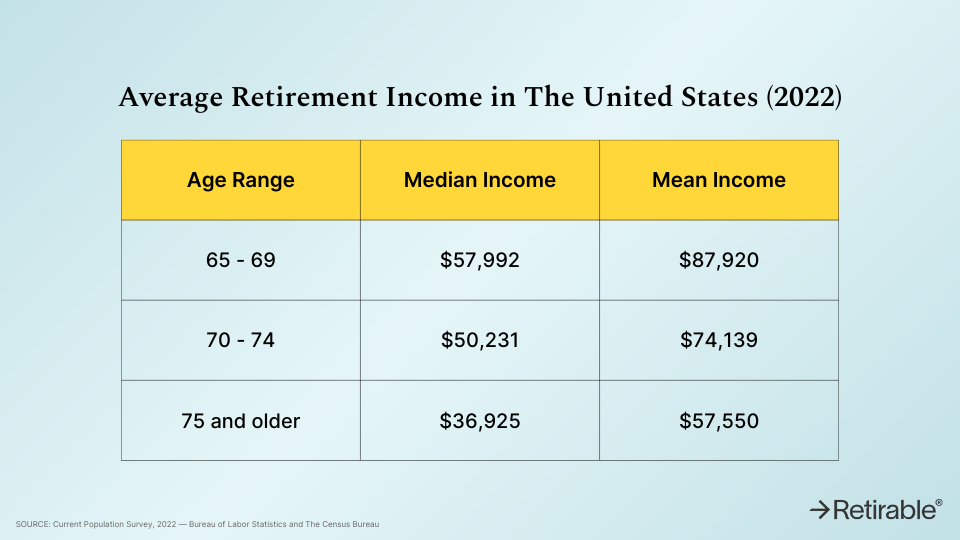
When you retire and start receiving your pension income, you might wonder if you still need to pay National Insurance (NI) contributions. The short answer is no, you do not have to pay NI on your pension income. Let’s dive into the details and understand why.
Understanding National Insurance Contributions
National Insurance is a tax-based system that provides contributions towards various state benefits, such as the State Pension, Jobseeker’s Allowance, Employment and Support Allowance, and Maternity Allowance. It is paid by employed and self-employed individuals who meet specific criteria based on their income levels.
There are different classes of NI contributions, each with its own set of rules and rates:
- Class 1 Contributions: Paid by employees and their employers on their earnings from employment.
- Class 2 Contributions: Flat-rate contributions paid by self-employed individuals with profits above the Small Profits Threshold.
- Class 3 Contributions: Voluntary contributions to fill gaps in your National Insurance record.
- Class 4 Contributions: Paid by self-employed individuals on their profits from self-employment.
While you are working and earning an income from employment or self-employment, you are required to pay the appropriate NI contributions based on your circumstances.
Pension Income and National Insurance
Once you reach State Pension age and start receiving your pension income, you no longer have to pay National Insurance contributions. This applies to all types of pension income, including:
- State Pension
- Workplace or occupational pensions
- Personal pensions (e.g., Stakeholder Pension, Self-Invested Personal Pension (SIPP))
- Annuity income
- Income drawdown from your pension pot
The reason you don’t have to pay NI on your pension income is that NI contributions are only collected on income from employment or self-employment. Pension income is treated differently and is not subject to NI contributions.
However, it’s important to note that while you don’t have to pay NI on your pension income, you may still be liable for Income Tax, depending on the amount of your pension and other sources of income.
Key Points to Remember
- National Insurance contributions are not payable on pension income, including State Pension, workplace pensions, personal pensions, annuity income, and income drawdown.
- NI contributions are only collected on income from employment or self-employment.
- You stop paying NI contributions when you reach State Pension age.
- If you continue working after State Pension age, your employer is still liable for employer’s NI contributions on your earnings.
- While you don’t pay NI on pension income, you may still have to pay Income Tax, depending on the amount of your pension and other sources of income.
By understanding the rules surrounding NI contributions and pension income, you can better plan your retirement finances and ensure you are not overpaying or underpaying taxes.
Should You Top Up Your NI Contributions For A Better State Pension?
FAQ
Does pension income count towards NI?
What income is subject to NI?
Will pension count as income?
What is the pension age in NI?