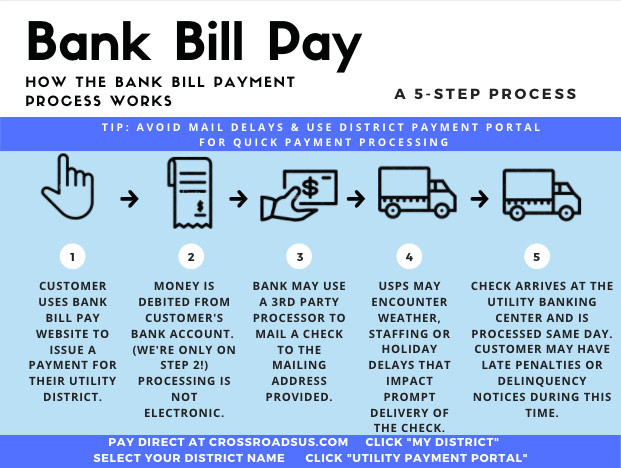
Bill pay makes life easier by automating payments for recurring expenses. However sometimes the recipient doesn’t cash the check you sent. This can create problems if bills show late or unpaid. Read on to learn what happens when bill pay checks aren’t cashed how to avoid issues, and steps to resolve uncashed checks.
Overview of Uncashed Bill Pay Checks
Bill pay services let you set up one-time or automatic payments to companies or individuals The bill pay provider prints and mails a check on your behalf With electronic bill pay, recipients typically cash checks quickly.
However, checks sometimes go uncashed if:
- The recipient loses or misplaces the check.
- There are address problems during mailing.
- The recipient fails to cash the check before it expires.
- There are issues processing and depositing the check.
If a bill pay check isn’t cashed, your account won’t reflect the payment. You could face late fees, service disruption, hits to your credit, or other problems if the bill remains unpaid from the vendor’s perspective.
Let’s explore common reasons checks aren’t cashed and your options for resolving uncashed bill payments.
Top Reasons Bill Pay Checks Go Uncashed
Bill pay checks can slip through the cracks for various reasons. Here are some of the most common:
-
Recipient overlooks the check: Checks get buried under piles of mail and missed. Or the recipient doesn’t check the mail frequently enough before a check expires.
-
Mailing address errors: If you enter an incorrect mailing address, the check is undeliverable. The USPS returns it to your bank.
-
Checks lost in transit: While rare, checks can also be lost or damaged by mail carriers before reaching the payee.
-
Payee changed addresses: If the recipient moved without notifying you or the post office, the check won’t forward to their new address.
-
You or the payee switched banks; now you can’t deposit funds because the bank account numbers are closed, wrong, or out of date.
-
Processing problems: Issuer delays, insufficient funds, account disputes, or fraud holds can create deposit issues.
-
Recipient doesn’t have the right ID: Some billers need a government-issued ID to cash business checks, which can be a problem.
-
Payee hesitancy: Wariness about accepting checks from individuals vs. companies also prevents cashing.
-
Expired checks: If checks aren’t cashed within 180 days, they’re no longer valid or negotiable.
Being aware of these common hang-ups helps address problems promptly.
Consequences of Uncashed Bill Pay Checks
Forgotten checks seem harmless, but they can create bigger headaches down the road:
-
Late fees and interest: Without your payment posting on time, companies charge late penalties and interest.
-
Service disruption: Utilities, cell phones, and other services might get cut off from non-payment.
-
Credit damage: Missed payments show up on credit reports, lowering your score.
-
Collections: After multiple months, unpaid accounts can get sent to collections agencies.
-
Supply issues: If vendors don’t receive your payment, they may halt orders and supplies.
-
Relationship impacts: Service professionals like contractors rely on prompt payment for their own expenses.
Financial uncertainty: You lose money as uncashed checks remain in limbo.
Act quickly when discovering uncashed checks to minimize hassles.
Steps To Take When Bill Pay Checks Go Uncashed
If your recipient hasn’t cashed a check past the due date, take these proactive steps:
-
Contact the recipient: Ask if they received the check and mention the due date. Have them verify the mailing address and cash it promptly.
-
Call your bank: Notify them of outstanding checks past 30 days. They may request a stop payment or issue a replacement check.
-
Place stop payments: Request stop payments on large uncashed checks to avoid potential fraud.
-
Update addresses: Change the recipient’s address in your contacts and bill pay profile to avoid repeat issues.
-
Pay via alternate methods: Switch to electronic payments or pay the vendor directly as a short-term workaround.
-
Dispute fees: If you incurred late fees, appeal to reverse them if you have proof of payment attempts.
-
Set reminders: Flag next payment dates to follow up with recipients quickly about uncashed checks.
-
Review bank policies: Understand processes regarding undeliverable checks, stop payments, and reissues.
With vigilance, you can minimize headaches from uncashed payments.
Stop Payments on Uncashed Checks
Placing a stop payment instructs your bank to block payment on the original check if cashed and lets you request a replacement. Follow your bank’s stop payment procedures, typically requiring:
-
The check date, number, and exact amount
-
The payee’s name
-
The account number
-
Stop payment fees (around $30 per check)
Timeliness matters since banks can only stop unpaid checks. Immediately report missing checks to maximize the likelihood funds remain unclaimed. Stop payments expire after 180 days but let you buy time to resolve problems.
Banks may automatically void outstanding checks after 90 days and credit your account. But don’t rely on this. Formal stop payments provide verification and let you control replacement checks.
Canceling and Reissuing Bill Pay Checks
If you requested a stop payment, your bank requires confirmation of a valid reason for reissuing the check, such as:
- Address discrepancies
- Processing delays and non-receipts
- Unrecoverable losses
- Payee errors like closed accounts
- Expired checks per bank policy
Your bank verifies the initial check is invalid. Then they debit your account again for the new check’s amount when printed and mailed.
Frequent reissues for similar reasons will, however, raise scrutiny to ensure validity. Know your bank’s limits on check replacements within a given timeframe.
When Recipients Refuse Checks
Getting declined is another reason bill pay checks go uncashed. Some recipients may:
- Only accept electronic payments or credit cards
- Require corporate checks from official business accounts
- Have policies against taking personal checks
- Want payment methods that generate receipts and records
If a recipient won’t accept your check, ask for acceptable alternate payment. Switch to money orders, account transfers, payment apps, or other suitable options moving forward. You may have to absorb fees for stop payments and new payment methods.
Best Practices To Prevent Uncashed Checks
Preventing problems with uncashed checks begins with smart bill pay management:
-
Maintain accurate mailing addresses for payees.
-
Discuss acceptable payment methods with recipients before sending checks.
-
Start bill pay transactions early to allow time for issues.
-
Track payments and follow up within 7-10 days of due dates.
-
Review bank statements monthly to identify uncashed items.
-
Set calendar reminders on outstanding checks approaching expiration dates.
-
Keep payees informed of any account or contact changes on your end.
-
Verify checks clear your bank within two statement cycles.
-
Utilize electronic bill pay instead of physical checks when available.
Closely monitoring bill pay activity protects you when checks go astray.
Options If a Check Remains Unresolved
If all efforts fail to resolve an uncashed check long-term, a few options remain:
-
Claim the funds: After 180 days, banks remove outstanding checks from your account balance with no payee claim.
-
Cancel the payment: Write it off as a loss if it was a smaller amount and the payee hasn’t pursued collection.
-
Pay again: For important obligations, pay via money order or new check. Let the payee know the situation.
-
Dispute billing penalties: Argue to remove late fees and interest since you attempted payment in good faith.
-
Consult your lawyer: They can advise on laws and rights if dealing with large, contested amounts.
-
File police reports: Reporting stolen or forged checks provides documentation to reverse liability.
How rigorously you follow up depends on the payment amount and payee relationship.
In Summary
While annoying, uncashed checks are manageable if handled quickly and correctly. Initiate communication and stop payments right away after a due date passes. Record details for all uncashed payments. Double check information entered in bill pay systems. And monitor bank statements routinely for problems. With some diligence, you can avoid major disruptions when recipients fail to cash your payments.
Have Other Questions? We Can Help!
Ope, thanks for stopping by!
By following this link, you’re leaving GateCity.Bank to visit an external site. While this site has been known for being completely safe, please know that we’re ultimately not responsible for its content.
Friendly reminder: Please don’t share Social Security numbers, account numbers, credit card numbers or passwords via email. If you need to share sensitive information, give us a call instead at 701-293-2400 or 800-423-3344 .
Alright, let’s get you going!
Stopping Payment On A Check Could Cost You Big
FAQ
How long is a bill pay check good for?
Can a bill pay check be cancelled?
How long does it take for a bill pay check to clear?
How to know if a bill pay check was cashed?