When it comes to healthcare coverage, understanding the difference between Medicare and Medicaid is crucial. These two programs are often confused, but they serve distinct purposes and have different eligibility criteria. In this comprehensive guide, we’ll explore the key distinctions between Medicare and Medicaid, helping you navigate the complex world of healthcare coverage.
Medicare: Federal Health Insurance for Seniors and Individuals with Disabilities
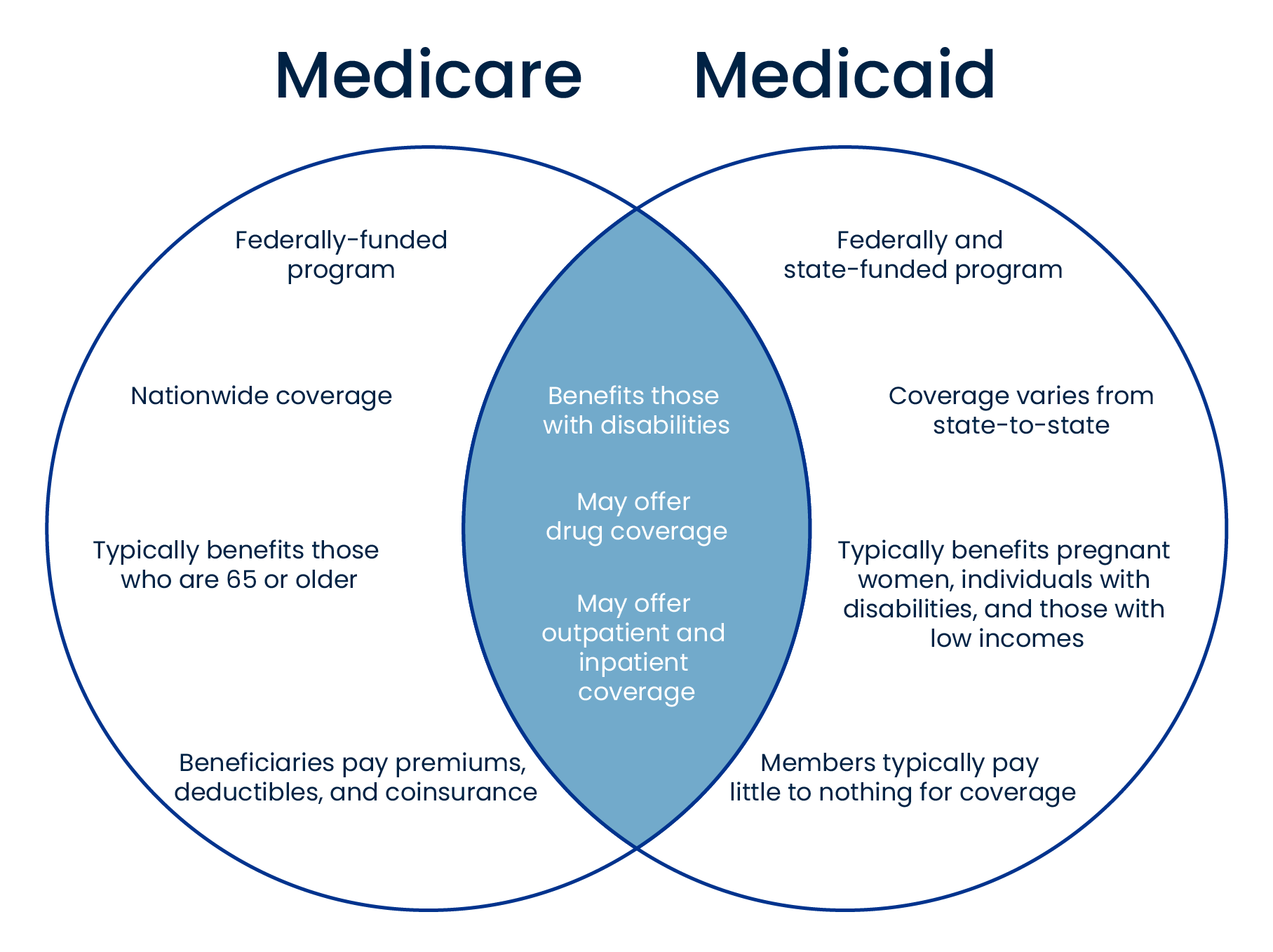
Medicare is a federal health insurance program primarily designed for individuals aged 65 and older, as well as some younger people with certain disabilities or end-stage renal disease (ESRD). This program is administered by the Centers for Medicare & Medicaid Services (CMS), a federal agency.
Here are some key features of Medicare:
- Eligibility: Most individuals become eligible for Medicare when they turn 65, regardless of their income level. However, younger individuals with specific disabilities or ESRD may also qualify.
- Coverage: Medicare consists of several parts, including Part A (hospital insurance), Part B (medical insurance), Part C (Medicare Advantage plans), and Part D (prescription drug coverage).
- Costs: While some parts of Medicare are premium-free, such as Part A for most beneficiaries, others require monthly premiums, deductibles, and coinsurance payments.
- Nationwide Coverage: Medicare coverage is consistent across all states, ensuring standardized benefits and costs for eligible individuals.
Medicaid: Joint Federal-State Program for Low-Income Individuals and Families
Medicaid, on the other hand, is a joint federal-state program that provides healthcare coverage to low-income individuals and families. Unlike Medicare, Medicaid is administered at the state level, with each state operating its own program under federal guidelines.
Here are some key aspects of Medicaid:
- Eligibility: Eligibility for Medicaid is primarily based on income and asset levels, which vary from state to state. Generally, the program covers individuals and families with limited financial resources, including children, pregnant women, elderly individuals, and those with disabilities.
- Coverage: Medicaid offers a comprehensive range of benefits, including inpatient and outpatient hospital services, physician visits, nursing home care, and home health services. However, the specific benefits may differ across states.
- Costs: Medicaid is designed to provide healthcare coverage at little or no cost to beneficiaries. However, some states may require small co-payments for certain services.
- State Variations: While the federal government sets broad guidelines, each state has flexibility in determining eligibility criteria, covered services, and provider reimbursement rates within their Medicaid program.
Key Differences Between Medicare and Medicaid
To summarize the key differences between Medicare and Medicaid:
| Aspect | Medicare | Medicaid |
|---|---|---|
| Eligibility Criteria | Age (65+) or specific disabilities | Low income and limited resources |
| Administration | Federal program (Centers for Medicare & Medicaid Services) | Joint federal-state program, administered by states |
| Coverage | Standardized across all states | Varies by state |
| Cost to Beneficiaries | Premiums, deductibles, and coinsurance | Little to no cost (some co-payments may apply) |
| Provider Reimbursement | Set by federal government | Set by each state |
It’s important to note that some individuals may be eligible for both Medicare and Medicaid, which is known as being “dual eligible.” In such cases, Medicaid may help cover certain costs not covered by Medicare, such as premiums, deductibles, and co-payments.
Navigating Healthcare Coverage Options
Understanding the differences between Medicare and Medicaid is crucial when exploring healthcare coverage options. If you’re approaching retirement age or have a disability, you may want to research Medicare eligibility and enrollment processes. For those with limited income and resources, exploring Medicaid options in your state can provide access to essential healthcare services.
It’s always advisable to consult with healthcare professionals, social workers, or government resources to ensure you understand the eligibility criteria, covered services, and costs associated with each program. By gaining a clear understanding of Medicare and Medicaid, you can make informed decisions and access the healthcare coverage that best suits your needs.
What is the difference between Medicare and Medicaid?
FAQ
What is the difference of Medicare and Medicaid?
What is the highest income to qualify for Medicaid?
How do I know if I have Medicare?
Who is not eligible for Medicare?