Serving in the military reserve components can open up educational benefits through the GI Bill, But how much does the GI Bill actually pay if you are in the Reserves or National Guard? The details matter when accessing this earned benefit,
An Overview of GI Bill Benefits
The GI Bill is made up of various programs offering education assistance to veterans, service members, and their families Two of the main options are
-
The Montgomery GI Bill – Selected Reserve (MGIB-SR) is for Reserve members who have agreed to serve for six years.
-
Post-9/11 GI Bill – For those who served on active duty after September 10, 2001. Some Reserve service may qualify.
Both programs give you a monthly payment while you go to an approved school or training program. How much you get depends on your GI Bill program, how long you train, and the type of program you choose.
Payment Rates for the MGIB-SR
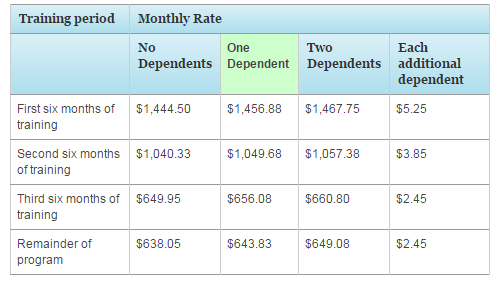
The MGIB-SR is designed for members of the Reserve components. Here are the current monthly payment rates:
Full-time enrollment – $466
3/4-time enrollment – $349
1/2-time enrollment – $233
Less than 1/2-time enrollment – $116.50
The full-time rate of $466 per month is for those enrolled in 12+ credits per term for undergraduate studies or 9+ credits for graduate programs at colleges and universities.
For vocational programs not leading to a degree, full-time is considered 22+ clock hours per week. Anything less is pro-rated down to the 1/2-time and less than 1/2-time rates.
These MGIB-SR rates apply to:
- Army, Navy, Air Force, Marine Corps, and Coast Guard Reserves
- Army National Guard
- Air National Guard
The Reserve components determine who is eligible for the MGIB-SR. You must have a 6-year service commitment signed up for this GI Bill program.
Comparing Post-9/11 GI Bill Payments
Active duty service members and some Reservists may qualify for the Post-9/11 GI Bill rather than the MGIB-SR.
The Post-9/11 GI Bill also provides monthly payments, but they are calculated differently based on your length of service, rate of pursuit, and the type of school.
Here are some key differences vs. the MGIB-SR:
-
Payments are issued directly to the veteran, not the school.
-
The housing allowance is based on the school’s location vs. a standard rate.
-
There is an annual book stipend up to $1,000 per year.
-
Tuition and fees are paid directly to public schools (veterans get any remaining balance).
-
There is a maximum tuition benefit per academic year equal to the highest public in-state undergraduate rate.
-
Eligibility is based on cumulative active duty service time after 9/11/2001.
While the Post-9/11 GI Bill offers generous benefits, the MGIB-SR provides a guaranteed base payment rate while on Reserve duty.
Payment Amounts Based on Training Time
One factor that determines your monthly GI Bill benefit is your training time or rate of pursuit. Here are some scenarios:
-
A Reservist taking 5 credits per semester qualifies for 50% of the full-time monthly rate.
-
A veteran going to school half-time while working qualifies for 50% of the Post-9/11 housing allowance.
-
A Reservist on active duty orders for part of the month may receive a prorated MGIB-SR payment.
-
Apprenticeship programs have varying rates based on time in the program.
The general rule is your payment decreases as your training time decreases for both GI Bill programs. The training time charts explain the qualifying thresholds.
GI Bill Monthly Rates Based on Program Type
The type of education or training program also impacts monthly GI Bill payments. Here are the categories to understand:
Colleges and Universities
-
Full monthly rates from both GI Bills apply when pursuing an undergraduate, graduate, or professional degree as a full-time student.
-
Approved programs include: vocational certifications, bachelor’s degrees, master’s degrees, law degrees, medical degrees, PhD programs, and more.
-
Public schools allow the Post-9/11 GI Bill to cover in-state tuition and fees.
Vocational and Non-College Degree Programs
-
Both GI Bills pay monthly benefits for attending vocational schools, technical schools, flight schools, and non-college degree programs.
-
To qualify for full rates, you must meet hourly requirements for classroom, lab, or shop time.
-
Examples are HVAC technician, welding, truck driving, cosmetology, and paralegal training programs.
On-the-Job and Apprenticeship Training
-
Monthly GI Bill payments are available for approved on-the-job training (OJT) and Registered Apprenticeships.
-
The MGIB-SR and Post-9/11 GI Bill have their own rates based on hours worked for OJT.
-
For apprenticeships, the monthly rates are assigned based on the length of time in the program.
Correspondence and Online Programs
- Both GI Bills pay reduced benefits
Using Your GI Bill
Your GI Bill can be used to pay for many different programs including the following:
Keep Up With Your Education Benefits
Whether you need a guide on how to use your GI Bill, want to take advantage of tuition assistance and scholarships, or get the lowdown on education benefits available for your family, Military.com can help. Subscribe to Military.com to have education tips and benefits updates delivered directly to your inbox.
Jim Absher is Military.coms former benefits editor and columnist. He joined the Navy to see the world and later realized the world is two-thirds water. He also worked for the Department of Veterans Affairs in field offices and Washington, D.C. before coming to Military.com in 2015. Read Full Bio © Copyright 2024 Military.com. All rights reserved. This article may not be republished, rebroadcast, rewritten or otherwise distributed without written permission. To reprint or license this article or any content from Military.com, please submit your request
GI Bill for National Guard & Reservist | How to Get 100%
FAQ
How much do you get from GI Bill reserves?
How much money does the GI Bill give you?
Do the reserves get VA benefits?
What is the GI Bill kicker for the reserves?
How does the reserve GI Bill work?
(U.S. Air Force photo) The monthly rates for the reserve GI Bill change each October, based on government calculations of higher education costs. You receive different amounts depending on what your “training time” is. If you are taking undergraduate classes your training time is determined as follows:
How much does GI Bill Pay?
Here are the key components: 1.**Tuition and Fees**: The GI Bill can pay your **full tuition and fees** at school.The exact amount depends on the type of institution you attend (public, private, or foreign)
What GI Bill benefits are available?
GI Bill benefits are available for Selected Reserve and National Guard members to help with education and training costs. The guide topics include the following: The Montgomery GI Bill Selected Reserve (MGIB-SR), is available to members of the Army, Navy, Air Force, Marine Corps, and Coast Guard Reserves, as well as the National Guard.
What is the Montgomery GI Bill Selected Reserve Program?
The Montgomery GI Bill Selected Reserve program offers up to 36 months of education and training benefits. If you’re a member of the Army, Navy, Air Force, Marine Corps or Coast Guard Reserve, Army National Guard or Air National Guard, you may be eligible for MGIB-SR. The amount you will receive depends on:
