When it comes to securing your family’s financial future, life insurance is a vital consideration. However, navigating the maze of policy types and options can be overwhelming. In this comprehensive guide, we’ll demystify the four main types of life insurance, empowering you to make an informed decision that aligns with your unique needs and goals.
Term Life Insurance: Temporary Protection at Its Finest
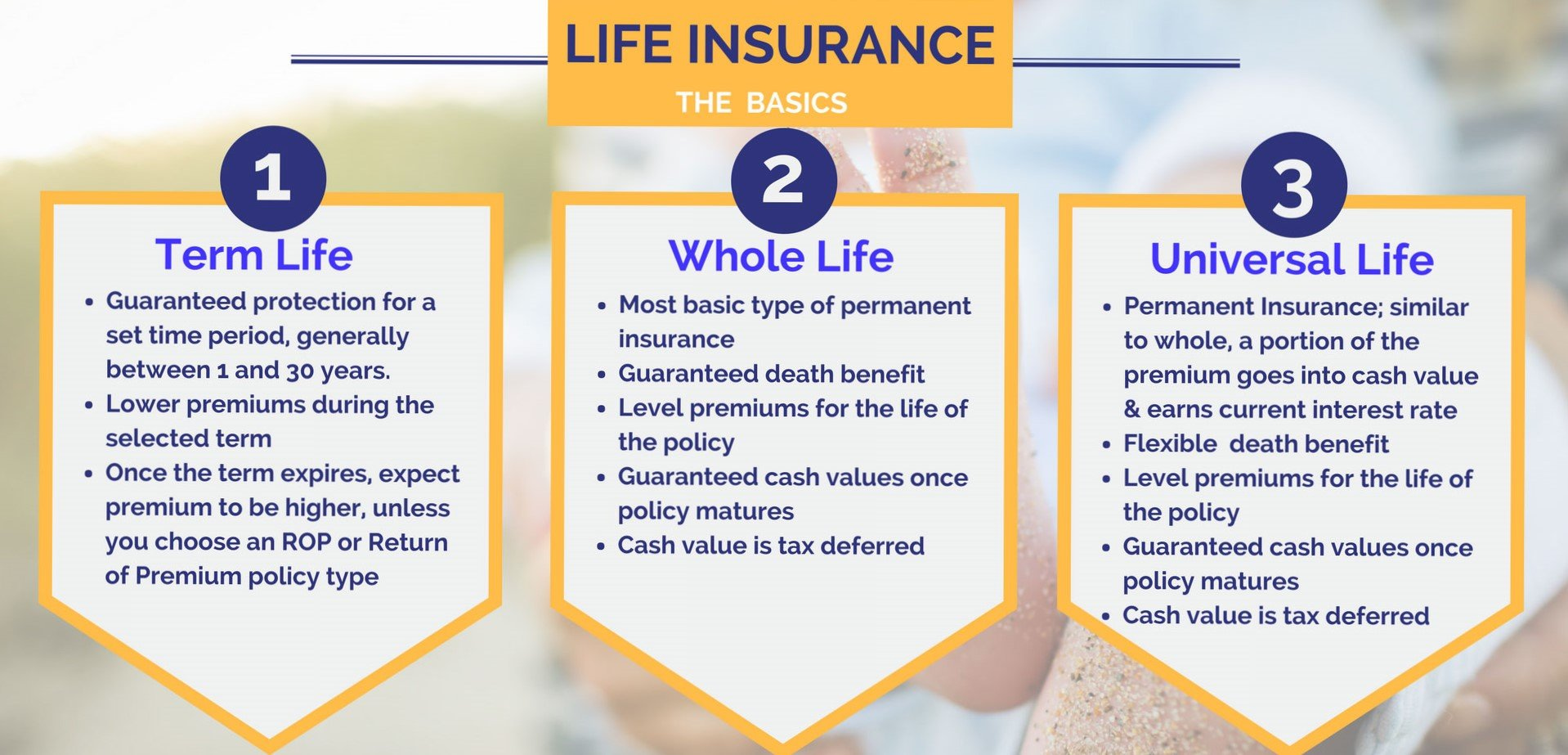
Term life insurance is often considered the most straightforward and affordable option. As the name suggests, it provides coverage for a specific term or period, typically ranging from 10 to 30 years. This type of policy is ideal for those seeking temporary protection during their prime working years or until their financial obligations, such as mortgages or children’s education expenses, are met.
The key advantages of term life insurance include:
- Affordability: Term life insurance premiums are generally lower compared to other types of life insurance, making it an attractive option for those on a tight budget.
- Simplicity: These policies are straightforward, with a fixed premium and death benefit amount throughout the term.
- Flexibility: You can choose the coverage amount and term length that suits your specific needs and budget.
However, it’s important to note that term life insurance does not accumulate any cash value, and if you outlive the term, you’ll need to either renew the policy (typically at a higher premium) or purchase a new one.
Whole Life Insurance: Lifelong Coverage with a Cash Value Component
Whole life insurance, as the name implies, provides coverage for your entire lifetime as long as premiums are paid. Unlike term life insurance, whole life policies build cash value over time, which can be accessed through loans or withdrawals. This cash value component can serve as a source of funds for emergencies or supplement retirement income.
The advantages of whole life insurance include:
- Lifelong protection: As long as you continue paying premiums, your beneficiaries will receive the death benefit, regardless of your age at the time of passing.
- Cash value accumulation: A portion of your premiums goes into a tax-deferred cash value account, which grows over time based on the insurance company’s investment returns.
- Guaranteed death benefit: The death benefit amount is guaranteed and will not fluctuate based on market conditions.
However, whole life insurance policies tend to be more expensive than term life insurance, especially in the early years, as a portion of the premiums goes towards building the cash value component.
Universal Life Insurance: Flexibility at Its Core
Universal life insurance offers more flexibility than whole life insurance, allowing you to adjust your premiums and death benefit amounts as your circumstances change. Like whole life insurance, universal life policies also accumulate cash value, but the growth is typically tied to the insurer’s portfolio investment returns or a money market rate.
The key advantages of universal life insurance include:
- Flexible premiums: You can increase or decrease your premium payments within certain limits, giving you more control over your cash flow.
- Adjustable death benefit: You can raise or lower the death benefit amount as your needs change, subject to the insurer’s guidelines.
- Cash value growth potential: The cash value component can potentially grow faster than whole life insurance, depending on the underlying investment performance.
However, it’s important to note that the cash value growth and death benefit are not guaranteed, as they are influenced by the insurer’s investment performance and other factors.
Variable Life Insurance: Tapping into Investment Opportunities
Variable life insurance is a type of permanent life insurance that allows you to invest the cash value component in various investment options, such as stocks, bonds, and mutual funds. This gives you the potential for higher returns but also carries increased risk, as the cash value and death benefit can fluctuate based on the performance of your chosen investments.
The key advantages of variable life insurance include:
- Investment opportunities: You have the flexibility to allocate your cash value among a range of investment options, potentially leading to higher growth compared to traditional whole life or universal life insurance policies.
- Tax-deferred growth: The cash value component grows tax-deferred, allowing your investments to compound more efficiently.
- Lifelong coverage: As long as you pay the required premiums, your beneficiaries will receive the death benefit, regardless of your age at the time of passing.
However, variable life insurance policies tend to be more complex and expensive than other types of life insurance. Additionally, the cash value and death benefit are not guaranteed and can fluctuate based on the performance of your chosen investments.
Making the Right Choice
Selecting the appropriate life insurance policy is a personal decision that hinges on your financial circumstances, risk tolerance, and long-term goals. Consider factors such as your age, income, debts, dependents, and existing assets when evaluating the different types of life insurance.
If you’re seeking temporary coverage during your working years or until specific financial obligations are met, term life insurance may be the most cost-effective option. For those seeking lifelong protection and the potential for cash value accumulation, whole life or universal life insurance could be a better fit.
For individuals with a higher risk tolerance and a desire for greater investment opportunities, variable life insurance may be worth exploring, but it’s essential to understand the associated risks and complexities.
Regardless of the type of life insurance you choose, it’s crucial to review your policy regularly and make adjustments as your life circumstances evolve. Consulting with a qualified financial advisor can help you navigate the complexities of life insurance and ensure that your coverage aligns with your long-term goals and objectives.
Types Of Life Insurance Explained
FAQ
What is the most common type of life insurance?
What are the 3 main types of life insurance?
What is the best life insurance policy to get?
Is term or whole life insurance better?